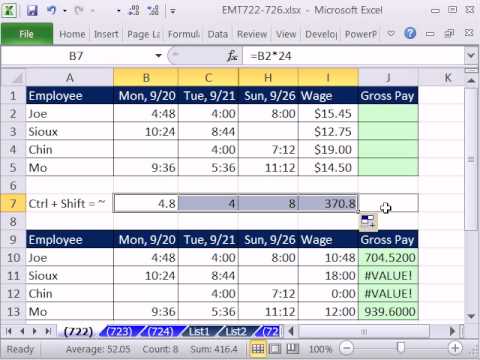
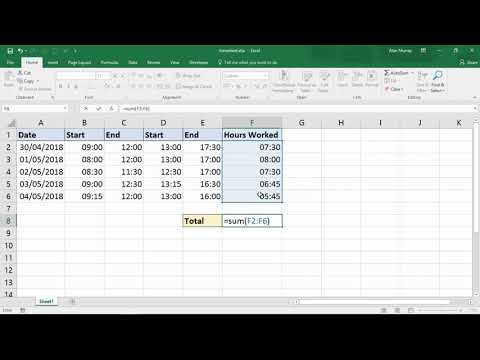
I paid my employee for 43 hours of wages during the last workweek. Eight of those hours were paid as sick leave, as the employee was out ill for one day. Am I required to pay the employee for three hours of overtime?
The required overtime pay is 1.5 times the hourly rate for hours worked in excess of 40 in a workweek. Overtime is calculated based on hours actually worked, and your employee worked only 35 hours during the workweek. Unless a policy, contract or collective bargaining agreement states otherwise, you needn´t count sick leave, vacation time, holidays, or other paid time during which the employee did not actually work. My employer paid me for 43 hours of wages during the last workweek. Eight of those hours were paid as sick leave, as I was out ill for one day.
Overtime is calculated based on hours actually worked, and in this scenario you worked only 35 hours during the workweek. Unless a policy, contract or collective bargaining agreement states otherwise, you do not get overtime pay if you used sick leave, vacation time, holidays, or other paid time and did not actually work. To determine your regular rate, divide the amount of your weekly salary by the number of hours worked during the week for which you are calculating your overtime pay. For instance, if your weekly salary is $500 and you worked 50 hours in one workweek, you would divide 500 by 50, giving you a regular rate of $10 per hour.
You use this regular rate to calculate your overtime pay just as you would with an hourly rate. Your employer would owe you $10 per hour for the first 40 hours and $15 per hour for the 10 hours of overtime, for a total of $550. Non-exempt employees are employees that are entitled to minimum wage as well as overtime pay under the FLSA. Employers are also required to pay these workers an overtime rate of 1.5 times their standard rate when they work more than 40 hours per workweek. A non-exempt employee that is not paid overtime wages can file an FLSA overtime claim through the U.S.
Most workers that are paid an hourly wage fall under this category. To properly compute overtime on a flat sum bonus, the bonus must be divided by the maximum legal regular hours worked in the bonus-earning period, not by the total hours worked in the bonus-earning period. This calculation will produce the regular rate of pay on the flat sum bonus earnings. Overtime on a flat sum bonus must then be paid at 1.5 times or 2 times this regular rate calculation for any overtime hour worked in the bonus-earning period. Overtime on production bonuses, bonuses designed as an incentive for increased production for each hour worked are computed differently from flat sum bonuses.
To compute overtime on a production bonus, the production bonus is divided by the total hours worked in the bonus earning period. This calculation will produce the regular rate of pay on the production bonus. Overtime on the production bonus is then paid at .5 times or 1 times the regular rate for all overtime hours worked in the bonus-earning period. Overtime on either type of bonus may be due on either a daily or weekly basis and must be paid in the pay period following the end of the bonus-earning period.
The Fair Labor Standards Act, passed in 1938, guarantees employees compensation at one and a half times their regular rate for hours worked above 40 hours per week. How overtime is calculated depends on whether the employee is paid hourly or by salary. Further, the calculation for salaried employees differs depending on the number of hours per week the salary is meant to compensate for.
When calculating annual hours for salaried employees, the math will be slightly different. Salaried workers receive checks weekly or bi-weekly, depending on the company. Those who are paid weekly should be covered for 40 hours, and those who are paid bi-weekly should be covered for 80 hours if that's a company's full-time policy. The employer must also be aware of holidays and vacation days and deduct those from the hours worked in the pay calculation. Not only that, but not only subtractions can be made — additions can be made as well, for working overtime, or on the sixth or seventh day of the week.
It is a fact of life that humans are unpredictable, but unfortunately, contracting officials get saddled with predicting their actions in order to draw up a reasonable contract. It is up to the employer to choose whether to pay biweekly or semi-monthly, but however a paycheck is issued, employers will need to know the employee's per-hour rate to determine their pay in a given period. Any unpaid holidays or vacation days should be deducted from the hours used in the pay period calculation.
The number of work hours in a year can be useful when figuring out an employee's yearly pay for a salary or to calculate salary into an hourly rate if schedules are changing. To figure out an employee's yearly pay for a salary, just multiply the suggested hourly rate by the number of work hours in a year. Your business may choose to pay for vacation days or even holidays and if that is the case, you will need to use the number of hours in a year before subtracting vacation days or holidays. For example, if Juan earns $23 an hour, works 40 hours a week, gets 10 holidays off a year and 14 vacation days per year, he should earn $47,850 if he receives paid holidays and vacations.
If he gets paid vacation days, but holidays are unpaid, he should earn $46,010 ($47,850 less his hourly rate multiplied by the 8 hours from each of the 10 holiday days). If all of his vacation days and holidays are unpaid, he should receive $43,434 ($47,850 less his hourly rate multiplied by the 8 hours from each of the 24 holiday and vacation days). OT Overtime The Time Card summary shows regular work hours and overtime hours. Employees are providing an average of two months of work to employersfor free every year. Any employee who works in excess of 38 hours per week or 7.6 hours in a day must be paid overtime.
Managers can discipline employees for not following company overtime policies – but business owners can't deny employees overtime pay. Overtime wages must be paid no later than the payday for the next regular payroll period after which the overtime wages were earned. Yes, there are certain types of payments that are excluded from the regular rate of pay. A group rate for piece workers is an acceptable method for computing the regular rate of pay.
In using this method, the total number of pieces produced by the group is divided by the number of people in the group, with each person being paid accordingly. The regular rate for each worker is determined by dividing the pay received by the number of hours worked. For this to be helpful, you'll need to decide what your pay period is. Or you can determine your hourly rate for a shorter period of time, such as a month or a few weeks. Is there a maximum number of hours employees can work during a day? For most adult workers, there are no limits on daily work hours.
Theoretically, employers may schedule employees to work seven days a week, 24 hours per day, so long as minimum wage and overtime laws are observed. Manufacturing employees are limited to 13 hours of work in a 24-hour period. There are also daily and weekly limitations on the hours minors can work. For more information, see the Oregon Wage & Hour Laws handbook.
It's easy to calculate the number of work hours in an entire year by multiplying the number of hours in a workweek, times the number of weeks in the year. Forty hours a week worked times 52 weeks is 2,080 hours worked per year. However, not every employee works a straight 40 hours – you'll have to add up their totals and multiply those by the number of weeks in a year to get the individual's annual total. When calculating annually for employees, make sure to take other factors into account as well. Most works usually have some holidays and vacation days, which you'll need to subtract from their total work hours. In the U.S., according to the payment rules regulated by the Fair Labour Standards, salary workers are not covered by overtime .
It is worth mentioning, that in many countries companies offer their workers various kind of compensations for overtime hours. That might be just additional money, time off adequate to the number of overtime hours, or other benefits. When a salaried employee is classified as non-exempt under Fair Labour Standards, an employer has to pay one and a half for each extra hour over standard 40 per week.
There are a few jobs which are exceptions from that rule . To avoid misunderstandings, clear all your doubts in your state's Department of Labour or your country's labour law. Salary to hourly wage calculator lets you see how much you earn over different periods. It is a flexible tool that allows you to convert your annual remuneration to an hourly paycheck, recalculate monthly wage to hourly rate, weekly rate to a yearly wage, etc. This salary converter does it all very quickly and easily, saving you time and effort. In the article below, you can find information about salary ranges, a closer look at hourly and annual types of employment, as well as the pros and cons for each of these.
Moreover, you can find a step-by-step explanation of how to use this paycheck calculator down below. The agreed upon regular hours must be used if they areless thanthe legal maximum regular hours. For example, if you work 32 to 38 hours each week, there is an agreed average workweek of 35 hours, and thirty-five hours is the figure used to determine the regular rate of pay. If in making these calculations you discover that your regular rate is less than minimum wage, your employer is in violation of minimum wage laws.
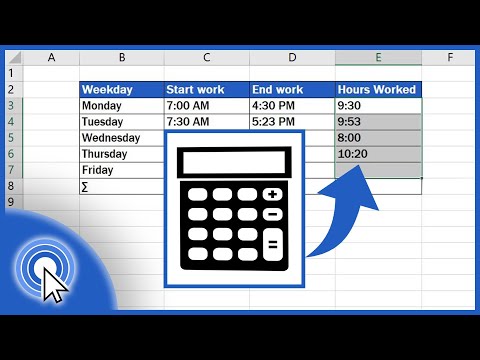
There are basically two ways to calculate the hours per month. With full-time employees, you should assume one employee will work a 40 hour workweek. A quick and easy method of calculating monthly hours is to multiply 40 hours per week by 4 weeks, yielding 160 hours for the month. If the employee does not work the same number of hours every day, enter the average number of hours per day the employee works.
Working days per week Enter the number of days the employee works per week. The days will default to 5 days a week, but can be modified. Average working hours per month This value will be used to calculate the rate per hour. Average working days per month This value will be used to calculate the rate per day. Working days per period are usually 20, 21, 22 or the average of 21,67.
Annual salary, Fixed salary, Rate per day, Rate per hour Enter any one of these values according to the employee's employment contract. This employee must not be paid unless hours or days worked are advised Select this option if the employee's salary must not be paid by default. The system will require input of hours or days before a salary is calculated. Use this option for employees who, for example, have to submit a time sheet of hours worked.
To translate a person's salary into an hourly rate, simply divide the yearly salary by the number of work hours in a year. Again, remember to include any vacation or holiday hours that the employee is paid. For example, if Alicia earns $72,000 a year, works 40 hours a week and gets 7 paid holidays and 10 unpaid vacation days, she would work a total of 2,000 hours .
Freelancers' earnings are usually based on hourly or daily rates though, sometimes, they are based on weekly or monthly payments. And since working as a freelancer doesn't come with the many benefits that full-time employees enjoy, their pay must be higher than what full-time employees would relatively earn. In our contemporary supply-demand-driven environment, however, we often see that the rates are under pressure. Take, for example, a salaried employee who is paid $500 in salary for a 50-hour workweek and works a 50-hour week. The first step, as before, is to calculate the Regular Rate. However, the Overtime Hours—the hours between 40 and 50—have already been compensated by the salary.
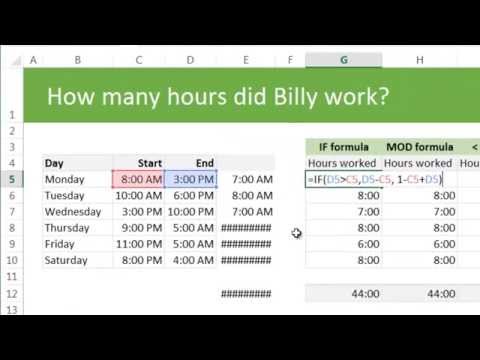
How Do I Figure Out My Hours Worked In effect, the employee has been paid $10/hour for those Overtime Hours. Thus, in calculating the overtime pay cannot be calculated by multiplying the Regular Rate by 1.5 because the employee has already received part of what he is entitled to. Salaried EmployeesSalaried employees are also entitled to overtime pay under the FLSA. The first step in calculating overtime pay for these employees is to determine the Regular Rate by diving the weekly salary by the number of hours it is intended to compensate. So, for example, the Regular Rate for a salaried employee who makes $400 for a 40-hour week is $10/hour ($400/40 hours).
Overtime pay for piece work can be calculated in two ways. Your employer can pay you one and a half times the piece rate for each piece completed during overtime hours, or you can use the "regular rate" calculation to determine overtime pay by the hour. Employees who worked less than 40 hours per week on average during a specific calculation period will have their average hours worked on a weekly basis added together. Divide this total number with 40, and then round the total to the nearest tenth to get the total FTE. Generally, the exemptions discussed above only apply to "white collar" employees.
No matter how highly paid non-management employees in production, maintenance, or construction are, they are entitled to a minimum wage and overtime pay. This includes professions such as carpenters, electricians, mechanics, plumbers, ironworkers, craftsmen, and construction workers. Is it correct to pay overtime when the employee works more than 80 hours in the two-week pay period? Your pay periods are irrelevant to the overtime calculation.
Pay periods may be established for any period not exceeding 35 days, but overtime must be calculated based on a recurring, seven-day workweek. If a workweek overlaps two pay periods, pay any overtime due for that workweek at the end of the second pay period . For example, if payday is on the 15th and the workweek ends on the 17th, the amount of overtime will not be known for that workweek until the following payday.
In other words, pay the overtime on the 30th -- the regular payday for the period in which the workweek ends. Can my employer offer me "comp" time off instead of paying overtime? Only government agencies are permitted to offer compensatory time in lieu of overtime. If you are a private sector employee, you must received overtime pay when you work over 40 hours in a workweek. Your employer can discipline you for violating its policy by working overtime without the required authorization.
However, wage and hour laws require that you are compensated for hours you work. Is there a maximum number of hours I can work during a day? From the people at Calculator Soup, this free time card calculator keeps track of work hours, breaks and pay on a daily, weekly or monthly basis.
It allows multiple breaks per day and can auto-deduct breaks from your total hours worked. This article reviewed a lot of options for tracking employee time. Department of Labor does not enforce how employers track employee hours, it does provide guidelines to track employee hours accurately. Regulations that state how long an employer must retrain payroll related data. Currently, employers are required to retain timecards and payroll related calculations for at least two years during and after employment. A complete list of wage-related information is located on the Department of Labor website dol.gov.